The ongoing cost of living crisis, marked by rising inflation, increasing energy costs, and stagnant wages, has far-reaching effects beyond household budgets. Businesses across the UK are facing significant challenges as they navigate this economic turbulence. This article explores how the cost-of-living crisis impacts businesses, focusing on operational costs, consumer behaviour, and workforce management.
Rising Operational Costs
One of the most immediate impacts of the cost-of-living crisis on businesses is the increase in operational costs. Several key factors contribute to this surge:
- Energy Costs: The dramatic rise in energy prices has substantially increased the cost of running businesses. For many companies, particularly those in energy-intensive industries such as manufacturing and hospitality, higher energy bills have squeezed profit margins, forcing some to scale back operations or seek alternative energy sources.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Inflation and rising fuel costs have led to increased prices for raw materials and transportation. Supply chain disruptions, exacerbated by global events and logistics bottlenecks, have further driven up costs. Businesses are facing higher prices for goods and delays, impacting their ability to meet customer demand promptly.
- Interest Rates: As the Bank of England raises interest rates to combat inflation, borrowing costs for businesses have increased. This has particularly affected small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that rely on loans for capital investments and day-to-day operations.
Shifting Consumer Behaviour
The cost-of-living crisis, coupled with the aftermath of the coronavirus pandemic, has led to significant changes in consumer behaviour.
- Reduced Spending: With higher living costs, consumers have less disposable income, leading to reduced spending on non-essential goods and services. Retailers, hospitality providers, and discretionary service businesses are particularly affected as consumers prioritise essential expenditures like food, housing, and utilities.
- Value for Money: Consumers are increasingly seeking value for money, opting for discounts, promotions, and lower-cost alternatives. Businesses must innovate and adjust their pricing strategies to remain competitive, often at the expense of profit margins.
- Digital Shift: The crisis has accelerated the shift towards online shopping as consumers look for convenience and competitive pricing. Businesses with strong e-commerce capabilities have an advantage, while those reliant on brick-and-mortar sales must pivot to digital platforms to capture consumer spending.
Workforce Management Challenges
Managing the workforce has become much more complex in recent years, with working from home and mental health now key considerations to taken whenever it comes to workforce management.
- Wage Pressures: As living costs rise, employees are demanding higher wages to maintain their standard of living. Businesses must balance the need to offer competitive salaries to retain talent with the financial strain of increased payroll expenses.
- Employee Wellbeing: The financial stress on employees can lead to decreased productivity, higher absenteeism, and mental health issues. Forward-thinking businesses are investing in employee wellbeing programs and flexible working arrangements to support their workforce.
- Labour Shortages: Certain sectors, particularly hospitality, healthcare, and logistics, are experiencing acute labour shortages. The cost-of-living crisis has exacerbated these shortages as workers seek better-paying opportunities or leave the workforce due to financial pressures.
The Difficult Decision: Closing a Business
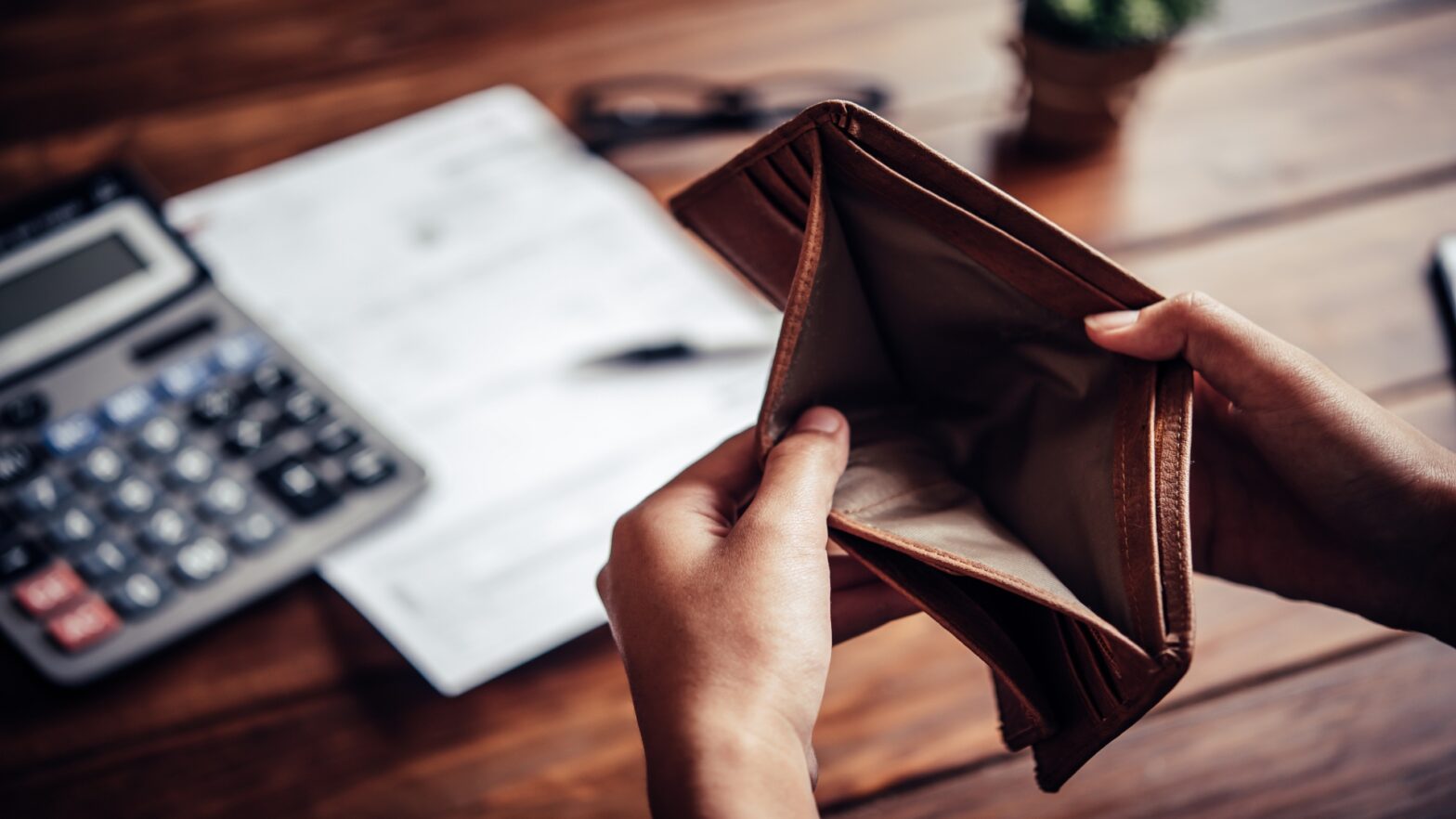
For some businesses, the cost-of-living crisis has led to a stark and painful reality: the need to close down. The decision to cease operations is never easy, but the ongoing economic pressures have made it an unavoidable outcome for many:
- Financial Unsustainability: Rising costs, reduced consumer spending, and mounting debts have rendered many businesses financially unsustainable. Despite efforts to cut costs and boost revenue, some companies find that they can no longer cover basic expenses, leading to insolvency.
- Insolvency and Liquidation: When a business can no longer meet its financial obligations, insolvency becomes a critical issue. In such cases, companies may need to enter administration or voluntary liquidation, which involves selling off assets to pay creditors. This process can be emotionally and financially draining for business owners and employees alike.
- Impact on Employees and Communities: The closure of a business has a ripple effect, impacting not only the owners but also employees, suppliers, and the local community. Job losses and the subsequent loss of income can have devastating effects on individuals and families, while the disappearance of a business can erode local economies, particularly in smaller towns and rural areas.
- Legal and Logistical Considerations: Closing a business involves navigating a complex legal and logistical process, including settling debts, handling employee redundancies, and complying with regulatory requirements. Business owners must seek legal and financial advice to ensure that the closure is managed as smoothly and ethically as possible taking into consideration the solvent position of the company.
Conclusion
The cost-of-living crisis continues to present significant challenges for businesses across the UK. Rising operational costs, shifting consumer behaviour, and workforce management complexities require businesses to be agile and adaptive. By implementing a good strategic response, focusing on innovation, and supporting their workforce, businesses can navigate these turbulent times and emerge stronger. As the economic landscape continues to evolve, resilience and adaptability will be key to sustaining business success.

Technology
25 March 2025
Ransomware-As-A-Service Variants on the Rise With Critical Infrastructure Providers at the Greatest Risk

Business Advice
25 March 2025
Claims Processing Automation: How Insurers Can Cut Costs and Improve CX

Technology
18 March 2025
Secret Signs Your Internet Security Has Been Compromised